Anisakis simplex
A Marine Parasite
Life Cycle and Interactions
Anisakis simplex has an extraordinarily complex life cycle for an organism so small. As a parasite, it utilizes more than one host, and can interact with several possible species to complete its stages of life. The stages of life, including hosts and reproduction, are as follows.
Adult
The parasite, Anisakis simplex, first resides as an adult within the intestinal mucosa of a marine mammal, such as a dolphin or porpoise. The females produce eggs that are then released through the excretory matter of the mammal into the water.
First Stage Larvae
Once the eggs enter the water, they first develop an embryo and shortly thereafter form into first stage larvae within the egg.
Second Stage Larvae
The first stage larvae molt and become
second stage larvae, hatch, and swim freely through the
water.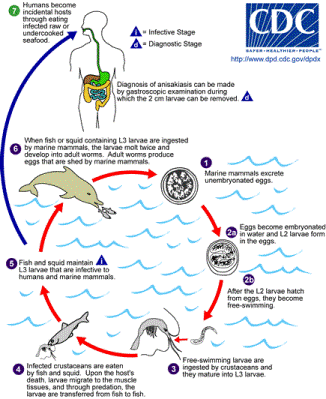
First Host, Third Stage Larvae
The free- swimming larvae are then consumed by a crustacean- their first host. The larvae then moves into its third larval stage, the first infective stage, and migrates to the first to the intestine. There, it grows, moving deeper into the peritoneal tissues, until the host is devoured by a predatory fish or squid.
Second Host, Third Stage Larvae
The parasite maintains the form of its third larval stage, as it is the only one that is infective, and makes its home in the intestine of the second host, the fish or squid. They continue to thrive in this environment, and may be passed on to other secondary hosts through predation. However, whenever the final second host dies, it penetrates the muscle tissue, as the second host is consumed by a larger organism.
Third Host, Third Stage Larvae and Adult
When the larger organism, which is either a marine mammal or a human, consumes the infected fish or squid, the third stage larvae moves into the gastric and intestinal mucosa and infects the mammal; it's third host. The larvae then sheds its present form by molting twice and morphing into an adult. At this point, the parasite can begin its vicious cycle all over again.